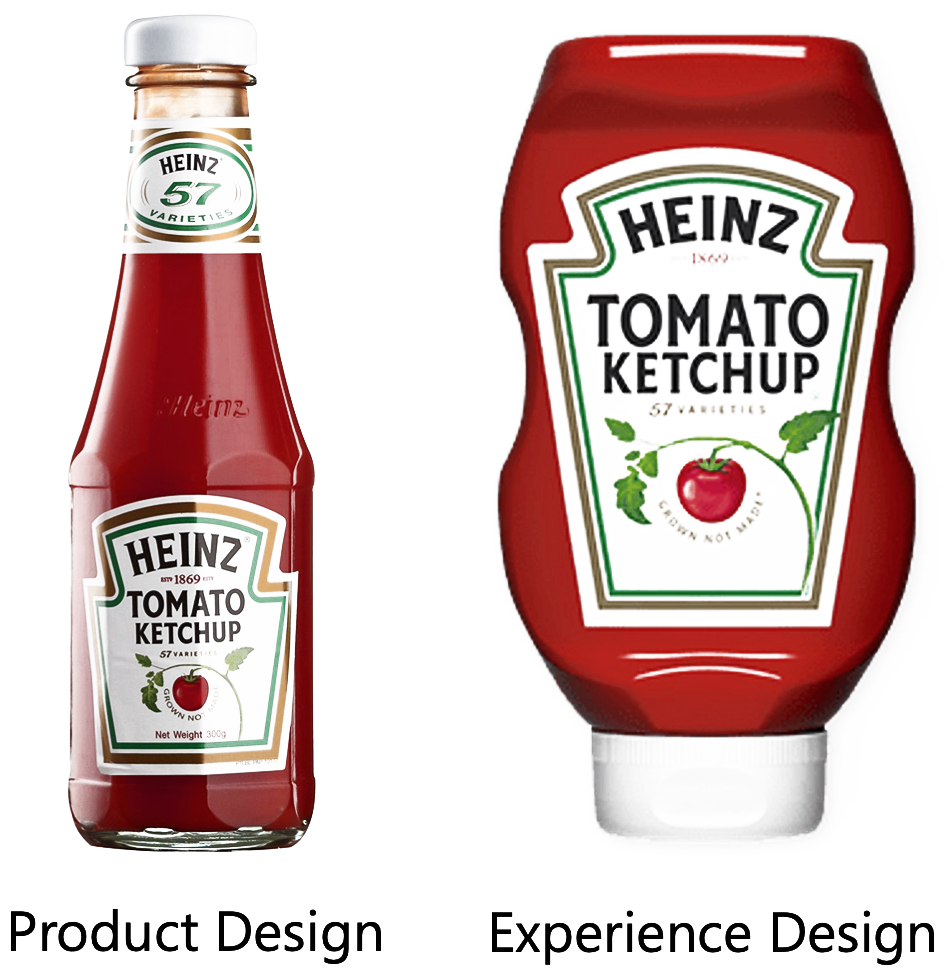
The Design Thinking Mindset
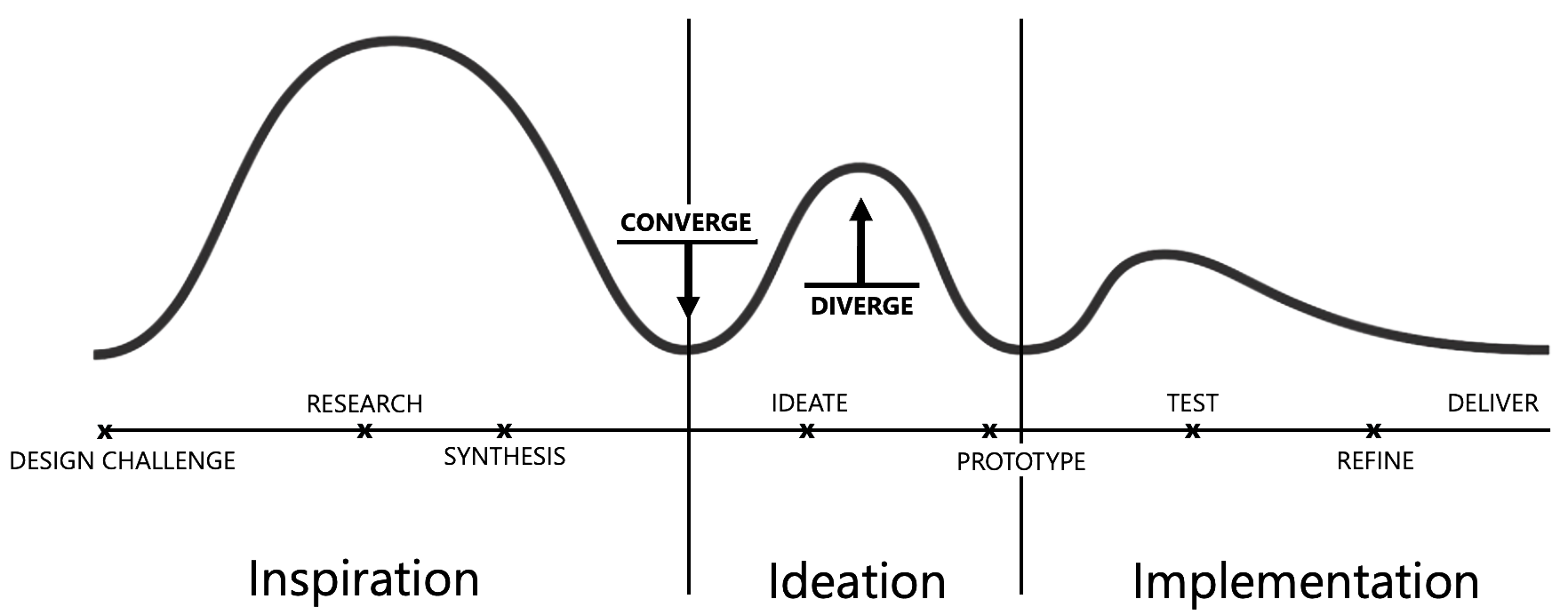
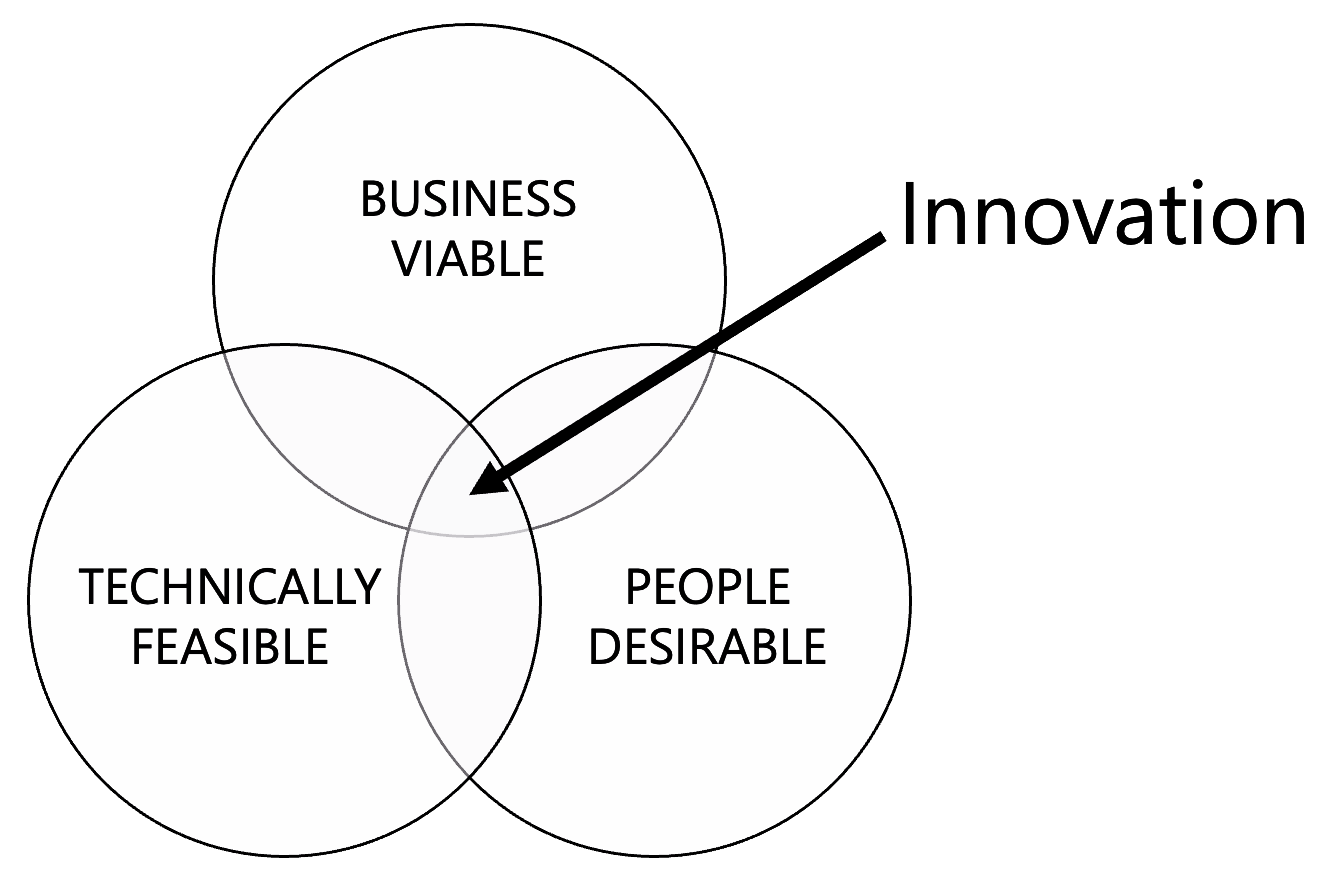
Innovision EQ subscribes to the IDEO model of design thinking methodology, which lays out an optimal philosophy for human-centered and data-driven design, and is comprised of three phases, each of which being revisited during the iterative process of product design and development, and during which divergent and convergent thinking enable designers to create choices, then make choices.
Inspiration
The first phase in design thinking is inspiration: defining the challenge. By casting a wide net and gathering as much data as possible about the current state of the targeted experience, we create a data set rooted in customer and product research. Depending on time restrictions and budget, this includes:
Quantitative Data
Analytics tools assess the full customer journey—from triggers to conversion, drop-off, or resolution.
Dashboards using Tableau, SQL data warehouses (BigQuery, Snowflake), and A/B testing platforms (Optimizely) measure product performance through OKRs, KPIs and critical moments along the journey.
Qualitative Data
Competitive benchmarking, insights from industry journals, i.e. J.D. Power, and exploring analogous digital experiences for ideas.
Customer focus groups, interviews, surveys, journey and empathy mapping, and ethnographic research reveal the language customers use, as well as pain points, unmet needs, and opportunities to simplify the experience along the journey.
Internal stakeholder interviews uncover obstacles and siloed communication issues.
Assessing app store reviews (Google Play, App Store) to gain real customer insights that inform the next phase—ideation.
Ideation
Once we observe all available data points - THE WHAT - we interpret and synthesize the data, drawing from it patterns and themes - THE WHY - that can be used in ideation. Not unlike a crime scene, a half-baked digital experience must be investigated down to anatomical and DNA levels for proper development, as inconclusive data yields inconclusive results.
Well-Crafted HMWs (How Might We) Questions set the team up for success, providing guard rails for ideation which target unmet customer needs and pain points.
Brain Storming Sessions: Teams dive into brainstorming, encouraging wild ideas and different perspectives to challenge the status quo head on, fostering innovation.
Prototyping: Quickly bringing ideas to life through prototypes allow teams to see how concepts work in practice. The motto? Build, test, repeat.
Exploration without Judgment: Explore multiple possibilities with an open mind—no idea is too outlandish. Innovation flourishes when judgment is parked at the door.
Collaboration and Feedback: Encourages cross-disciplinary collaboration and seeking feedback early and often to refine ideas.
Iteration: The process is iterative; refining ideas based on user feedback and testing them further to hone in on solutions that really click.
Implementation
The implementation phase is where ideas transition from concepts to reality, bringing innovative solutions to life:
Prototyping and Testing: Developing functional prototypes and testing them rigorously ensures they meet user needs and handle real-world scenarios. It’s where the rubber meets the road.
Iterative Refinement: Continuously refining and tweaking the solution based on feedback and testing results ensures the final product is polished and effective.
Pilot Launches: Roll out the solution in controlled environments to gather insights and making final tweaks.
Collaboration with Stakeholders: Working closely with all stakeholders, including marketing, engineering, and user support teams ensures seamless delivery and adoption.
Measurement and Adjustment: Using metrics and KPIs to evaluate performance post-launch enables the making of necessary adjustments to enhance product efficacy.
Design thinking is a human-centered approach that fosters innovation through three key phases: Inspiration, Ideation, and Implementation. This cyclical process promotes continuous learning, innovation, and improvement, making it effective in addressing complex challenges and delivering impactful solutions.